Describe the Anatomy of a Hair
The clinical significance of hair includes increased hair loss disorders complete hair loss disorders and other conditions. The hair shaft consists of a cortex and cuticle cells and a medulla for some types of hairs.

Hair And Nails Anatomy And Physiology I
Structure of Hair.

. The human hair is formed by divisions of cells at the base of the follicle. Hair is comprised of 3 layers these are as follows the cuticle the cortex and the medulla. Hair and Nails Hair.
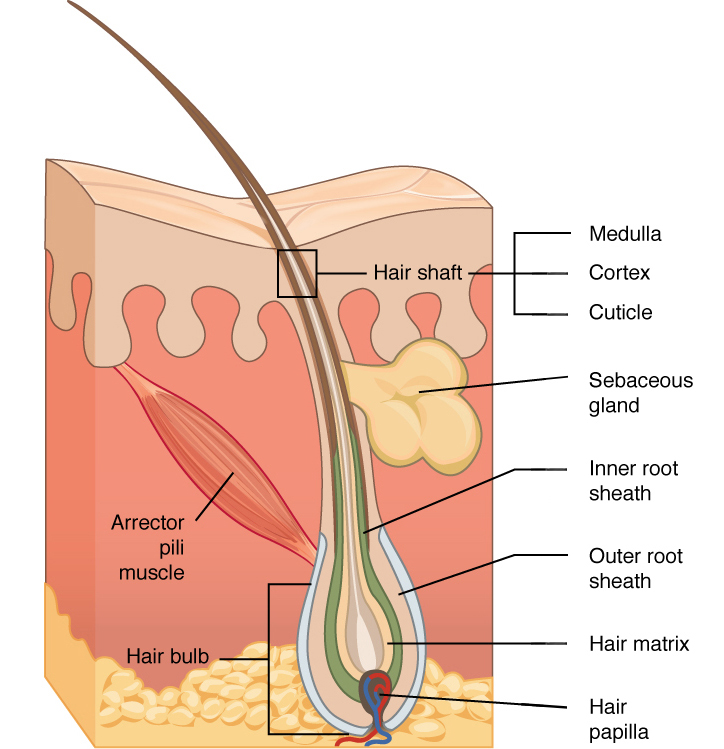
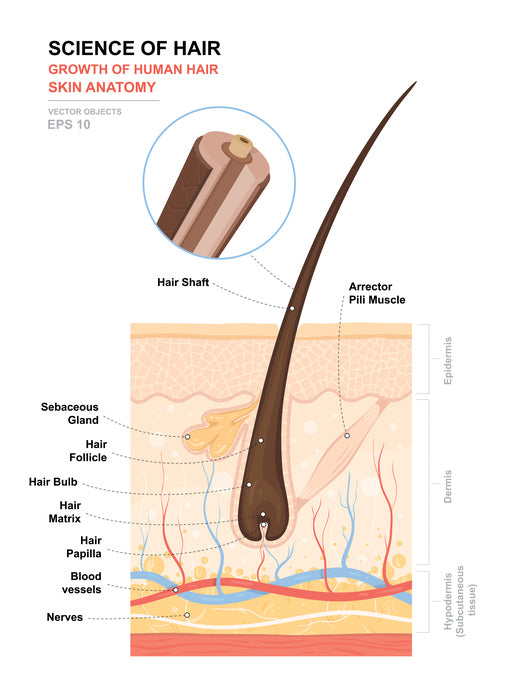
The follicle is the essential unit for the generation of hair. Graphic with the hair shaft hair root hair follicle hair bulb sebaceous gland arrector pili and dermal papilla. Each hair is composed of columns of dead keratinized epidermal cells bonded together by extracellular proteins.
Its a stocking-like structure that starts in the. Hair is a keratinous filament growing out of the epidermis. It is primarily made of dead keratinized cells.
These regions are illustrated in Figure 1 with some of the basic structures found in them. Hair structure a Describe in detail the structure of a hair identifying the 3 layers. When you are frightened cold or angry these small muscles contract causing your hair to stand on end.
Up to 10 cash back 1 Hair Bulb. The shaft is the visible part of the hair that sticks out of the skin. The shaft consists of three layers of keratin which are.
The anatomy of the hair bulb includes the components like matrix and the dermal papilla. The cuticle which is the outermost layer consisting of scale-like overlapping cells five to twelve deep. Anatomy of the Hair.
The hair root is in the skin and extends down to the deeper layers of the skin. Strands of hair originate from the base of the downward extension of. The hair is made up of 95 keratin a fibrous helicoidal protein shaped like a helix that forms part of the skin and all its appendages body hair nails etc.
The hair bulb forms at the base of the follicle and inside the bulb are living cells that divide and grow to build the hair shaft. Hair follicles originate in the epidermis and have many different parts. Lend itself to the evaporation and perspiration process.
The pilosebaceous unit comprises the sebaceous gland the arrector pili muscle and the hair follicle. Skin Glands and Secretions. Hair is a slender filament of keratinized cells that grows from an oblique tube in the skin called a hair follicle.
The hair shaft is the superficial portion of the hair which projects above the surface of the skin. The nail is a specialized structure of the epidermis that occurs at the tips of our fingers and toes. Smooth muscle that extends from the superficial dermis of the skin to the dermal root sheath around the side of the hair follicle What is the hair root plexus made of and location.
Cuticle This is the outer layer of the hair strand which protects the cortex. Solution for Describe the anatomy of a hair follicle. As the cells are pushed upward from the follicles base they become keratinized hardened and.
Strands of hair originate in an epidermal penetration of the dermis called the hair. The cause of alopecia is unknown. Dendrites of nuerons that surround each hair follicle What is the purpose of the hair matrix.
What layer of the skin can you technically find hair follicles in this one is tricky. The hair follicle is a tubelike pocket of the epidermis that encloses a small section of the dermis at its base. The hair usually grows back.
Hair follicle has a continuous growth and rest sequence named hair cycle. The hair shaft is the visible part of the hair. Help protect the skin.
Hair is part of the integumentary system. Hair serves to. Part of the hair that extends from epidermis Root part of the hair below the surface Medulla inner part of hair follicle Cortex major part of shaft most pigment Cuticle Outter layer of the hair scales Follicle external and internal root sheaths Papilla end of hair shaft blood vessels Matrix in statum basale growth - part of anatomy of hair.
The hair follicle is the stocking-like structure under the skin where your hair is. Each hair shaft also contains a small gland called the sebaceous gland located next to the hair shaft. It takes a lot to grow one strand of hair and we can see this when someones health is affected so is their hair.
The follicle and the hair shaft. Responsible for the growth of existing hairs. Keratin is synthesized by keratinocytes and is insoluble in water thus ensuring impermeability and protection for the hair.
The most common type of hair loss in men. While a strand of hair might seem thin in your hand its comprised of three layers. Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermisHair is one of the defining characteristics of mammalsThe human body apart from areas of glabrous skin is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hairMost common interest in hair is focused on hair growth hair types and hair care but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily.
A tiny muscle called the erector pili connects the lower portion of each hair shaft with the underside of the skin. It is formed from dead cells and gives the hair shaft strength and provides protection for the softer inner structures. Hairs are dead structures that are made of hardened protein called keratin.
The hair bulb is the head of the hair follicle that divides cells to make the hair shaft in a growth cycle and rest. Hair loss is often accompanied by psychological strife which should be addressed and monitored by clinicians12 While some. Round patches of total hair loss usually from the scalp.
Hair is a derivative of the epidermis and consists of two distinct parts. A hair can be defined as a slender thread-like outgrowth from a follicle in the skin of mammals. Male pattern baldness usually includes either a receding hairline hair loss at.
Hair is primarily comprised of a fibrous protein and contains a very small amount of lipids fats and water. Composed mainly of keratin it has three morphological regionsthe cuticle medulla and cortex. Each hair has a hair shaft and a hair root.
Help with the nerve sensing functions of the integumentary system. It is surrounded by the hair follicle a sheath of skin and connective tissue which is also connected to a sebaceous gland. The part of the hair follicle plays a vital role in the hair growth cycle.
Keratin provides the body with a protective toughness for its entire surface. Describe the structure and function of hair. The hair follicle is where your hair begins to grow and where its held in place.
Cortex The thickest layer of hair is the inner layer which is responsible for hair strength color and pigment and hair texture. The hair bulb is where blood vessels nourish and deliver hormones for growth.

Human Hair Anatomy Hair Follicle Anatomy Ny Hair Loss

No comments for "Describe the Anatomy of a Hair"
Post a Comment